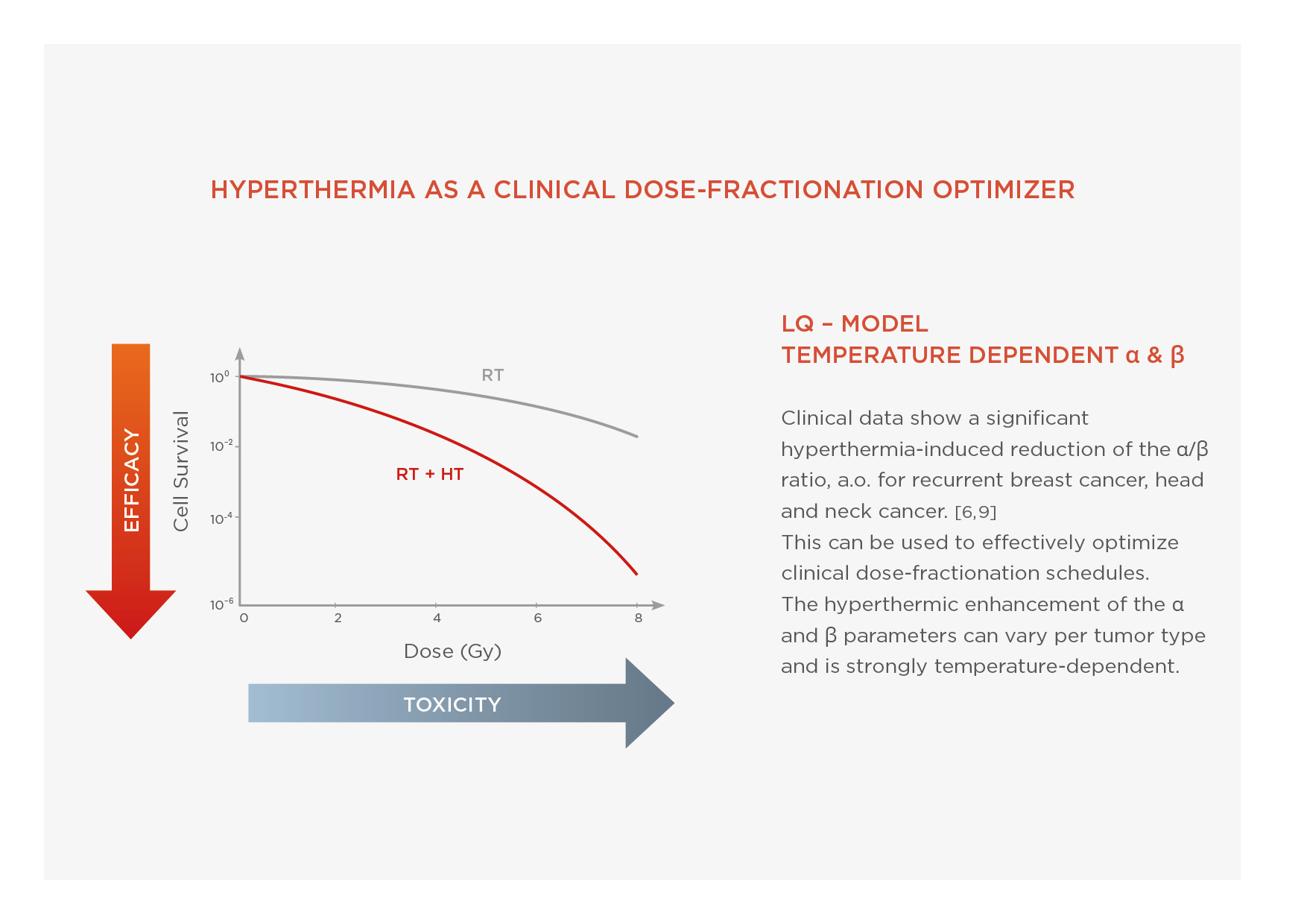
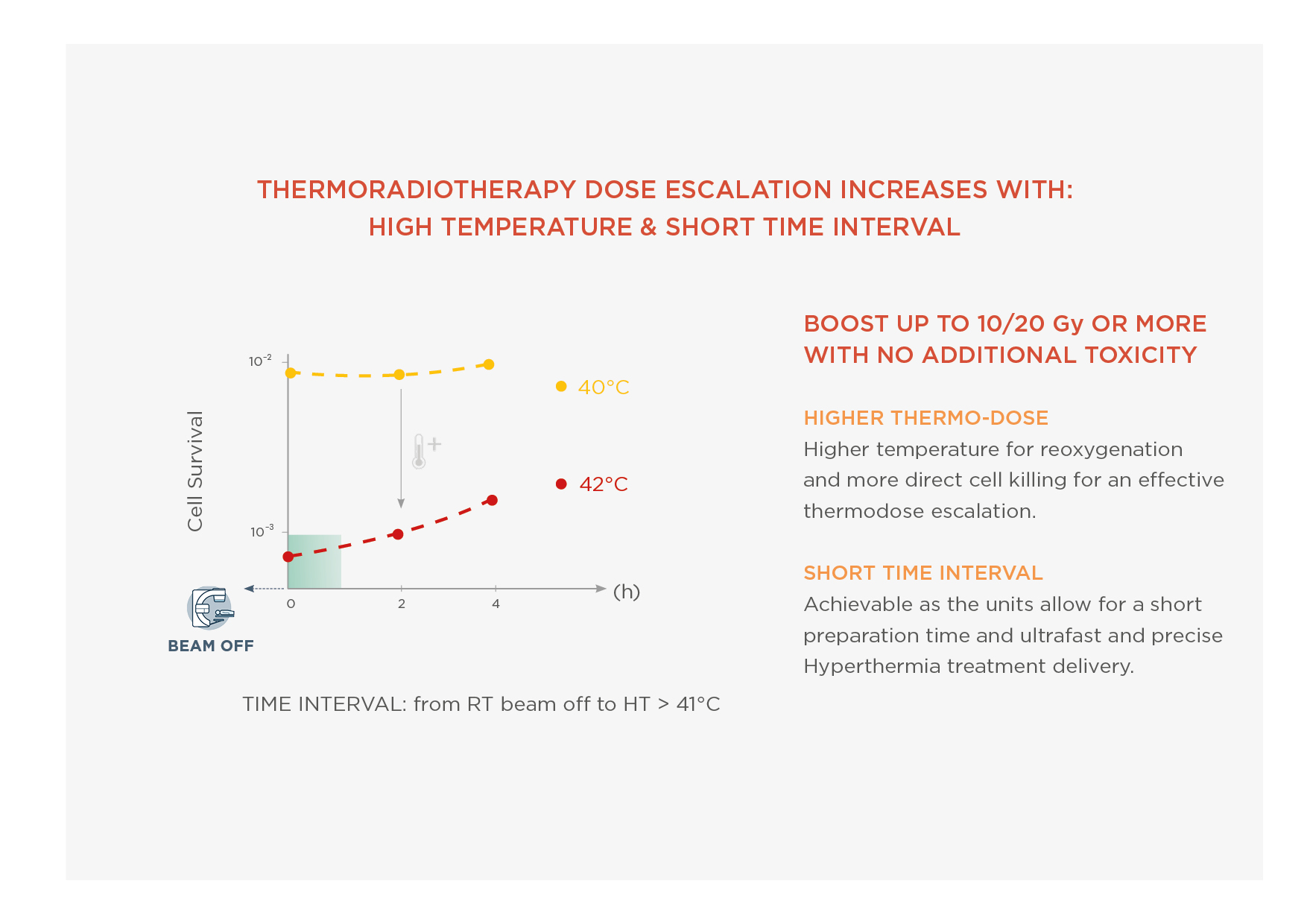
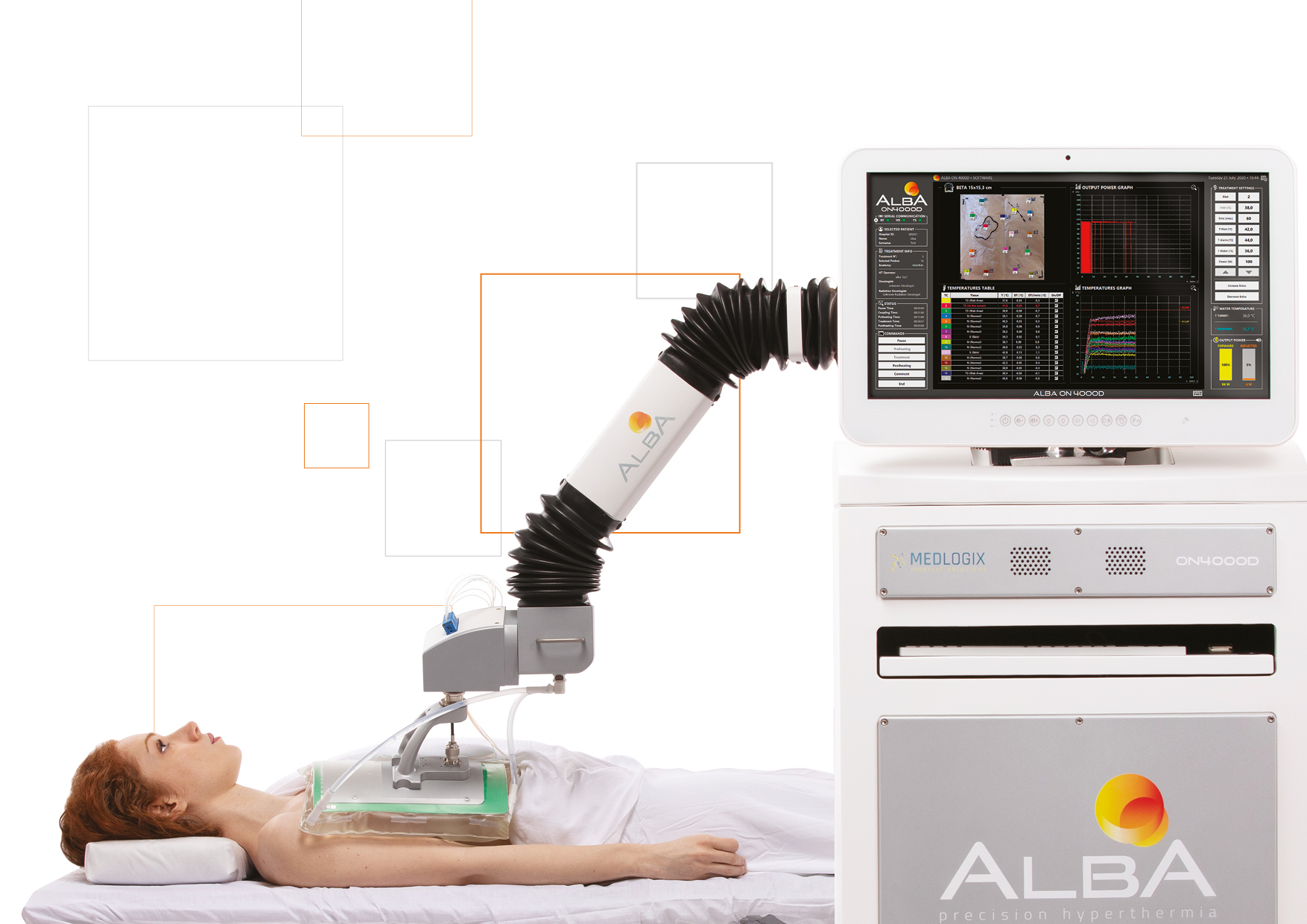
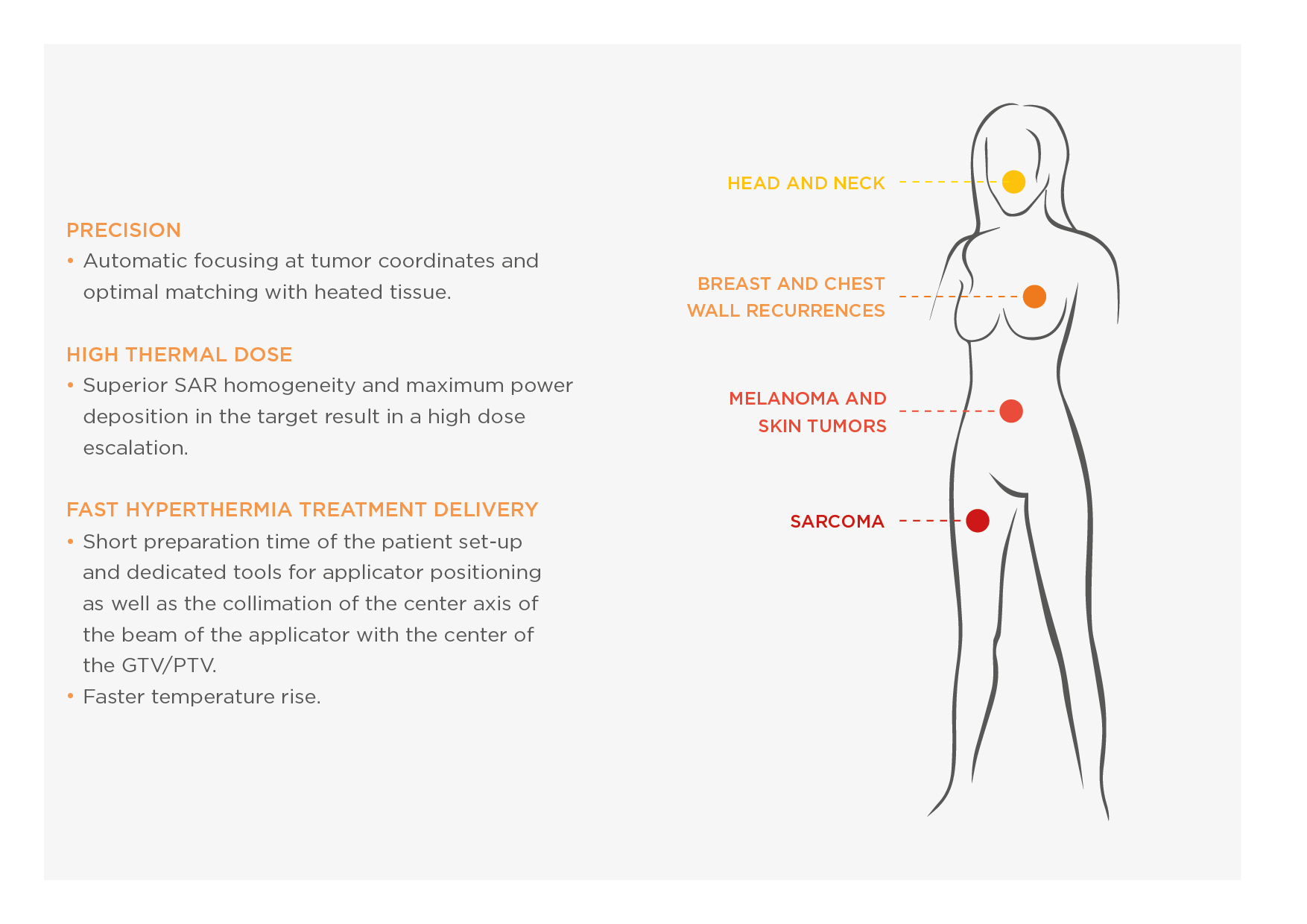
Hyperthermia (HT), heating tumors in the range 41-43°C, is a powerful radio and chemosensitizer. The effectiveness of HT as well as its safety, in combination with radiotherapy and chemotherapy, has already been proven in phase III clinical trials [1, 2] particularly in patients with very large or very advanced stages of cancer and recurrent tumors. HT enhances the effect of radiotherapy on the tumor, without additional toxicity for healthy tissues, thanks to of three synergistic mechanisms: